

The interviewer can use short hand and abbreviate responses. Normally, the recording should take place side by side. The interviewer 'can either write the response at the time of interview or after the interview. Recording - The last stage in an interview, is recording responses. However probing should be used carefully and should not bias the respondent's reply. Some of the frequently used probing styles are use of comments like "I understand", "Uh-huh", repeating the respondents reply to incite him to rethink his reply, give an expectant out pause to convey interest etc.
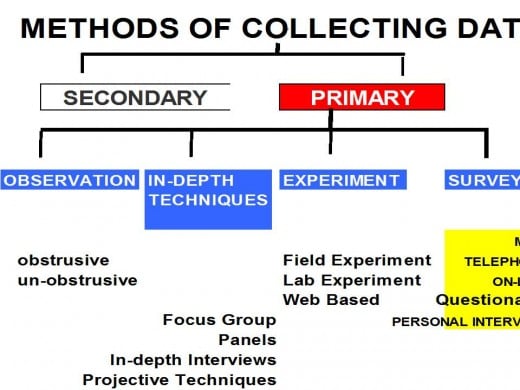
Probing is the technique of encouraging the respondents to answer freely, completely and relevantly. An advantage of interview is that it allows for probing. Generally the questions should be asked the way they are worded in order to avoid bias, but if they are not understood or heard properly they may be repealed. Probing - In this stage the interviewer collects data by asking questions from an interview schedule which contains questions in prearranged sequence. If the respondent is unavailable, then the interviewer should ensure that he seeks a reappoint. An introductory letter goes a long way in conveying the study's legitimacy. Introduction - An introduction involves the interviewer identifying himself by giving him his name, purpose and sponsorship if any. Wherever possible an appointment should be sought. It is important that the interviewer should convey his confidence to the respondent and satisfy his mental reservations if any. Hence in the initial stage the interviewer should increase the receptiveness of the respondent by making him believe that his opinions are very useful to the research, and the interview is going to be a pleasure rather than an ordeal. Rapport Building - The first reaction of a respondent on being asked to give interview is to say 'No'. Generally an interview should go through the following stages. Method of Conducting an InterviewĪ personal interview involves a lot of preparation. door to door interviewing where the respondents are interviewed in their home, or as planned formal executive meeting, most commonly used to interview officials and business persons, or as a mall intercept survey where respondents are interviewed at select places where the chances of finding respondents is maximum. The personal interviews can be conducted in many forms e.g. Generally the personal interview is carried out in a planned manner and is referred to as 'structured interview'. The interview techniques can be grouped in the following categories: Personal InterviewĪ Personal interview is a face to face way communication between the interviewer and the respondent. Interview can be classified into various types' viz., personal interview, telephone interview, focus group interview, depth interview and projective techniques also called as indirect interviewing. It is thus clear that interview is a verbal conversation between two people with the objective of collecting research relevant information from the respondent. Bingham and Moore have described interview as 'conversation with a purpose.' Lindsey Gardner, has defined interview as a 'two-person conversation, initiated by the interviewer for the specific purpose of obtaining research-relevant information and focused by him on the content specified by the research objectives of description and explanation. The research data can be classified as follows: InterviewĪ form of communication approach to collecting data from respondent's interview is to oral or verbal questioning. The researcher is allowed to use unstructured methods, at his discretion, to record data. A subjectivist approach, requires a hypothesis test, but is not that rigid in following the procedures. There is little or no latitude available to deviate from the stated procedures or questions. In this the hypothesis is tested using publicly standard procedure. An objectivist approach is a more rigid and scientific approach. A survey research can be objectivist or subjectivist in nature. Primary data, by definition is the date that has been collected first hand by the researcher specially for addressing the population at hand. The data required for a research can be primary or secondary in nature. Regression Intercept Confidence Interval.Process Capability (Cp) & Process Performance (Pp).Data collection - Questionaire Designing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
